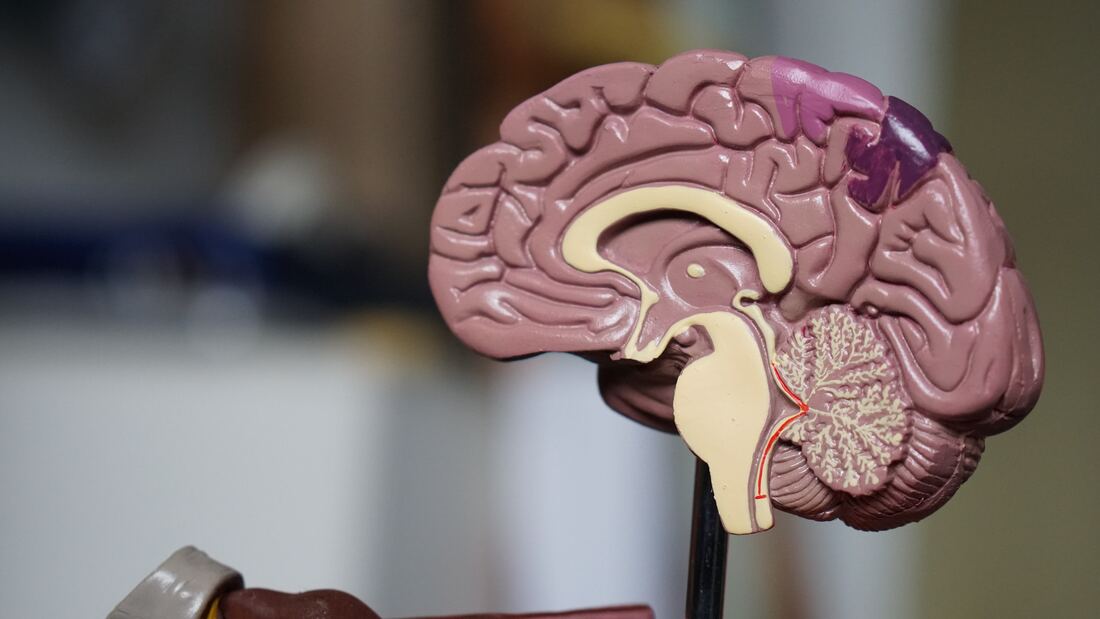
Worldwide, the NCBI estimates that one in five adults (17.6%) within the past year have struggled with a mood disorder (that is, any mental illness defined by the inability to regulate one's mood, such that it impacts one’s ability to function throughout the day), while 300 million (roughly 4.4%) individuals worldwide suffer from depression alone (1). The World Health Organization ranks depression as the single largest contributor to global disability, with anxiety disorders ranked as 6th. The sobering takeaway is that thousands of individuals struggle with mood disorders every single day, including anxiety, depression, PTSD, bipolar, and more. Chances are you have friends or family battling with some form of mental health disorder, or have struggled with one yourself. Even if you have had little to no exposure to mood disorders, the fact remains that you have still experienced anxiety, severe sadness, stress, and other difficult-to-manage emotions. In this post, we’ll explore CBD’s potential in aiding those with mood disorders. CBD and mood disorders Remember last week's post about the Endocannabinoid system? It’s laregly by virtue of this system that CBD and other endocannabinoids have such potential in treating some of the underlying causes of mood disorders. This is because CBD works through multiple pathways, affecting specific pathways in the brain associated with mood regulation. How it works *it’s important to know that most of the studies referenced below are animal studies, meaning that we still do not entirely know the effects of CBD on the human brain. That being said, the research is promising, and the potential for CBD in treating mental disorders is vast. The animal studies below strongly suggest multiple ways in which CBD may be effective in treating neuropsychiatric illnesses. Depression is an immensely complex condition. There is no single underlying cause, and we have much to learn in the way of treating it. According to the Institut Pasteur, 30% of patients are resistant to conventional treatment, including pharmaceutical SSRIs and MAOIs (2). In recent years, our understanding of neuroinflammation and its connection to depression has grown immensely. Neuroinflammation, inflammation of nervous tissue in the brain, is now considered to be one of the major underlying causes of depression- paving the way for new and potentially more effective methods of treatment. CBD has been shown to reduce neuroinflammation substantially (3), making it a potentially highly viable treatment for depressive disorder. Moreover, CBD has been shown to increase the health and function of the hippocampus (4), a part of the human brain responsible for mood regulation. Studies have shown that individuals suffering from mood disorders often have damage in the hippocampus region of the brain. One common cause of structural degeneration and impaired functioning in the hippocampus is chronic stress and anxiety, which may lead to an increase in susceptibility to neuropsychiatric disorders. While more longitudinal research is needed, studies suggest that treatments reversing stress-induced degeneration of the hippocampus may be viable for addressing mood disorders. CBD has also been shown to affect receptors in our brain responsible for regulating the uptake of serotonin and potentially increasing the amount of serotonin in our brains, combating depression and anxiety caused by depleted levels of serotonin. (5)  CBD versus Pharmaceutical Medications *CBD is not a replacement for prescribed medications. If you are currently taking a pharmaceutical medication, talk to your doctor before taking CBD or any health supplement which may interact with your medication. Quitting pharmaceutical medications without the support and advice of your doctor may have severe adverse effects. Pharmaceutical medications have come a long way in treating mental health. That being said, there is a lot left to be desired. It’s like opening the hood of your car and pouring steering fluid everywhere, in the hopes that some of the fluid falls where it needs to go. Some of it may end up in the right place and your car may continue to function regularly, but it’s not exactly efficient. Not to mention the fact that pouring steering fluid in places that aren’t meant to be covered in steering fluid may have some seriously adverse effects. Medications act in a similar way- they treat the whole brain, only sometimes affecting and addressing specific pathways. They are largely inefficient methods of treatments, often causing a number of negative side effects, including Insomnia, sexual dysfunction, mood swings, and agitation (not to mention long-term side effects- a subject that we know very little about). CBD has not been shown to produce any such effects. One animal study found that while antidepressants often took weeks to work, CBD had ‘fast and sustained’ antidepressant effects (6). This can be immensely helpful for those unable to wait weeks before feeling the affects of treatment. Multiple other studies have found that CBD significantly reduced levels of anxiety in individuals suffering from anxiety disorders such as SAD (7). The bottom line There is still much to learn about the potential effects of CBD on mood disorders. As mentioned above, most of the studies referenced throughout this blog are animal studies, meaning that the findings in regards to effects on the human brain are merely preliminary. That being said, the research strongly suggests that CBD may be viable for treating mood disorders. As always, talk to your doctor before taking CBD or any health supplement. Citations
With the massive and sudden boom of the CBD industry it seems as if CBD is everywhere. We see it infused in products ranging from tinctures, creams, to toothpaste and beer, all boasting a wide array of benefits. It can be hard to believe that one single product can be effective in treating so many different conditions. In an age of consumerism and misinformation, being a skeptical and discerning consumer is crucial. Understanding what your buying and why is necessary for keeping yourself safe and spending your money wisely. So, is CBD snake-oil? Just another health industry fad, destined to blow over once the next trendy thing takes its place? In short, no! In this blog, we’ll go over what makes CBD such a powerful and wide-ranging product, demystifying one of the most significant medical discoveries of this century- the endocannabinoid system. Of course, it’s important to still be a discerning consumer. Check out this three part series about the drawbacks of the CBD boom, the benefits of CBD, and how to navigate through it all. Or jump straight to part 3, where I provide a quick and easy guide to buying CBD! *At the end of this post you can find a short and informative video by Dr. Kellie Raydon, ALLAY'S science advisor, briefly explaining the endocannabinoid system.* The Endocannabinoid System It all begins with the endocannabinoid system. The endocannabinoid system, also known as the ECS, is a complex molecular system found in the human body that works to maintain balance and homeostasis. It is composed of three main parts:
Endocannabanoids Endocannabinoids are molecules made endogenously in the human body, discovered by a group of scientists researching THC in the 1990s. The two main endocannabinoids produced in the body are anandamide and 2-AG. While most other molecules in our bodies are produced, packaged, and then stored for later usage, endocannabinoids are produced on demand- meaning that they are immediately used to address specific needs, and then broken down by metabolic enzymes. Cannabinoid Receptors Cannabinoid receptors are found all over the human body. They are masters of transmitting information, relaying data to our body's cells and stimulating the correct cellular responses (Jikomes 2019). The two main receptors are CB1 and CB2. The majority of CB1 receptors are found in nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, although some CB1 receptors can be found in other spots throughout the body. CB1 receptors can be found specifically in the cerebellum, basal ganglia, hippocampus and dorsal primary afferent spinal cord regions (cite)- parts of the brain which are responsible for coordination and voluntary movement, memory, pain regulation, cognitive function, and mood regulation (Glass, Faull, & Dragunow 1997). CB2 receptors are found in the immune system on white blood cells, in the tonsils, and in the spleen (Mayfeild Clinic). One key function of CB2 receptors in the immune system is the regulation of cytokine release, which plays a crucial role in inflammation. The regulation of this system is the reason CBD is such an effective and celebrated anti inflammatory! Metabolic enzymes Once the endocannabinoids carry out their function in our body, they are quickly broken down by metabolic enzymes. Enzymes play an important role in regulating our use of endocannabinoids- they ensure that these molecules don’t linger for much longer than they’re needed.  So, what does it do? The ECS can be found in nearly every system in our body, including our central nervous system, our GI system, our bones, reproductive organs, hormones, immune system, metabolism, and muscles (link). It plays a vast and crucial role in maintaining homeostasis throughout our bodies. Homeostasis: The Goldilocks Zone Often referred to as the ‘Goldilocks Zone,’ homeostasis is that state of being ‘just right'. The human body has a relatively narrow range of conditions under which it is able to thrive. Any system that works to maintain homeostasis helps our bodies maintain balance in response to external conditions which may threaten to throw off this balance. It keeps things just right- not too hot and not too cold. For our bodies to function at peak performance- to stay healthy and feel good- we have to remain as close to homeostatic balance as possible. The endocannabinoid system plays a crucial role in keeping the various systems of our bodies balanced. It is responsible for regulating organ function and maintaining homeostasis throughout the body.  How Cannabis interacts with the ECS You may still be wondering what this all has to do with cannabis. How exactly does cannabis interact with this system? While endocannabinoids are endogenous cannabinoids produced by our bodies, cannabinoids such as THC and CBD are simply non-endogenous cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. The reason we feel any effects from THC and CBD is because these cannabinoids interact with out ECS. THC, for example, binds to and activates CB1 receptors, producing a ‘high.’ The fact that cannabinoids interact with our own endocannabinoid system is the reason why the effects and benefits of cannabinoids such as CBD are so wide ranging. To be sure, THC and CBD interact with a number of receptors throughout our bodies- not just the receptors in our ECS. However- their ability to work in congruence with and support the ECS is the primary reason CBD has so many different, profoundly beneficial effects. Current research There’s still a lot we don’t know about the ECS, but the current research is promising. The role of the ECS is vast, and the potential of cannabinoids such as CBD is great. Current research suggests that CBD may be effective in treating:
… The list goes on and on. While more research is needed, countless studies have been published strongly suggesting the healing capabilities of CBD. The discovery of the ECS has the potential to change the medical landscape as we know it, and the team at ALLAY is excited to be at the forefront of this change- educating consumers, spreading the word about holistic health, and providing conscious and transparent CBD products! Citations
Glass, M, et al. “Cannabinoid Receptors in the Human Brain: a Detailed Anatomical and Quantitative Autoradiographic Study in the Fetal, Neonatal and Adult Human Brain.” Neuroscience, vol. 77, no. 2, Mar. 1997, pp. 299–318., doi:10.1016/s0306-4522(96)00428-9. Grinspoon, Peter. “Cannabidiol (CBD) - What We Know and What We Don't.” Harvard Health Blog, 27 Aug. 2019, https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/cannabidiol-cbd-what-we-know-and-what-we-dont-2018082414476. Jikomes, Nick. “What Is the Endocannabinoid System and What Is Its Role?” Leafly, 1 Oct. 2019, https://www.leafly.com/news/science-tech/what-is-the-endocannabinoid-system. Mayfield Clinic. “Brain Anatomy, Anatomy of the Human Brain.” Mayfieldclinic.com, https://mayfieldclinic.com/pe-anatbrain.htm. |
AuthorCBD AllAY Archives
November 2020
Categories
All
|
Shipping and Warm Weather policy: As our product is heat sensitive - we do not ship over weekends and or holidays during peak summer months. We contact all customers with shipping notifications and please store your product in a cool dry place.
Terms Of Service | Privacy Policy | Medical Disclaimer
The Information contained on this site is not intended to diagnose or treat any condition and should not replace medical advice. Always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Keep out of the reach of children.
This product should be used only as directed on the label. It should not be used if you are pregnant or nursing. Consult with a physician before use if you have a serious medical condition or use prescription medications. A Doctor’s advice should be sought before using this and any supplement dietary product. All trademarks and copyrights are property of their respective owners and are not affiliated with nor do they endorse this product.
This product should be used only as directed on the label. It should not be used if you are pregnant or nursing. Consult with a physician before use if you have a serious medical condition or use prescription medications. A Doctor’s advice should be sought before using this and any supplement dietary product. All trademarks and copyrights are property of their respective owners and are not affiliated with nor do they endorse this product.





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed